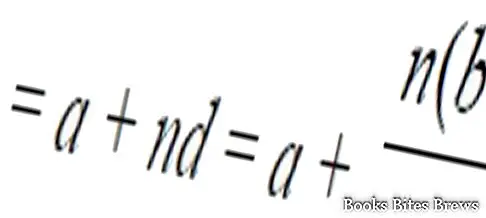Definition of algebra and arithmetic, what are the fundamental differences between these two fundamental branches of mathematics, useful notions to discover the importance of both.
Definition of algebra
Algebra is the branch of mathematics that deals with studying sets of any object, in which certain operations are defined in their form to be performed on the objects themselves.
There is a distinction between classical algebra and modern algebra.
The first definition indicates mainly the science of the equations obtained by equalizing one or more polynomials in zero in one or more indeterminate unknowns.
Contrary to geometry it is a relatively recent science, in fact the ancient Greeks used to translate every problem into geometric language.
For this reason, it was the Greeks who developed geometric algebra, managing to solve all the problems that can be translated into equations of the second degree.
From the ninth century on, the Arabs began to consider the equations from the numerical point of view, managing to find their solution through those calculation rules called in their entirety elementary arithmetic.
After the Arabs, the greatest development of arithmetic occurred in Italy in the sixteenth century, thanks to the discovery of general formulas useful for calculating the solutions of a third and fourth degree equation.
To achieve this goal, Italian algebraists introduced imaginary numbers and complex numbers.
The fundamental theorem of arithmetic establishes that an algebraic equation of degree n has exactly n roots, or solutions, in the context of complex numbers.
The birth of modern arithmetic is linked to Evariste Galois, who had the merit of reducing the study of algebraic equations to that of the groups of permutations associated with them, decisively deepening the general theory of groups.
Recommended readings- What are latitude and longitude, how are they calculated
- Antarctica: information, territory, Antarctic oasis
- What are the tallest skyscrapers in the world
- How to easily whitewash a room in the house
- How to make the perfect turn-ups for pants
Definition of arithmetic
By arithmetic we mean the part of mathematics that studies numbers.
The modern conception of the term includes the abstract science of numbers and the rules of calculation.
Arithmetic can be considered a theoretical science whose foundation dates back to the Pythagorean school.
The Pythagoreans in fact introduced the distinction between even and odd numbers, primes and compounds, also introduced proportions.
Their work was continued by Euclid, Archimedes, Eratostne and Diophantus.
Following the introduction of Arabic numeration in Europe, arithmetic experienced a huge development, which began in 1202 by Pisano with his "Liber abbaci and continued over the following centuries.
Elementary arithmetic is based on the four operations, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
This branch also includes proportions, fractions, root extraction, logarithms and irrational numbers.
Negative numbers and complex numbers are instead the subject of algebra.
Rational arithmetic concerns the search for independent axioms on the basis of which it is possible to construct arithmetic.
Higher arithmetic, now called number theory, indicated the evolution of elementary arithmetic, i.e. problems concerning divisibility, prime numbers, indeterminate analysis and arithmetic functions.